Menatto TM - Vitamin K2 (MK-7)
The Japanese Original
Developed through a natural fermentation process over 20 years ago, MenattoTM is the genuine Japanese vitamin K2 (MK-7). It is made in Japan, using a bacterial strain isolated from the traditional fermented Japanese food natto. It has been researched in Japan, by some of Japan’s most respected scientists. And it is distributed from Japan by J-Oil Mills, Inc., one of the leading edible oil producers in Japan with a history dating back to 1826. Welcome to The Japanese Original.
MenattoTM is produced through a natural fermentation process using B. subtilis natto, a beneficial bacterial strain used to make natto.

What is Vitamin K?
Vitamin K is a group of fat-soluble vitamins that are essential for various functions in the body, including blood clotting and bone metabolism.
There are three main forms of vitamin K: vitamin K1 (phylloquinone), vitamin K2 (menaquinones), and vitamin K3 (menadione).
Vitamin K1, also known as phylloquinone, is found predominantly in green leafy vegetables such as spinach, kale, and broccoli. It is involved in the synthesis of certain proteins that play a crucial role in the blood clotting process. When an injury occurs, these proteins help in the formation of blood clots to stop bleeding. Vitamin K1 is also important for maintaining healthy bones as it helps activate osteocalcin, a protein that binds calcium to the bone matrix, promoting bone mineralization and strength.
Vitamin K2, also known as menaquinones, has several subtypes, with the most studied form being MK-4 and MK-7. MK-4 is found in animal products like meat and eggs, while MK-7 is primarily derived from certain fermented foods, such as natto, a traditional Japanese dish made from fermented soybeans. Vitamin K2 is involved in calcium metabolism and plays a critical role in directing calcium to the bones and teeth while preventing excessive deposition in soft tissues, such as blood vessels. By keeping calcium out of arterial walls, vitamin K2 may help maintain flexibility and reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Vitamin K3, or menadione, is a synthetic form of vitamin K. It is not commonly used in dietary supplements due to its potential toxicity in high doses.
Vitamin K is absorbed in the intestine along with dietary fats and requires the presence of bile acids produced in the liver for optimal absorption. Absorption can be influenced by certain health conditions or medications that affect fat absorption or disrupt gut bacteria.
Deficiency of vitamin K is rare but can occur in certain conditions such as malabsorption disorders, liver disease, or with the use of certain medications that interfere with its metabolism. Symptoms of vitamin K deficiency may include easy bruising, excessive bleeding, and an increased risk of fractures.
The recommended daily intake of vitamin K for adults in India is generally around 55 micrograms (mcg) for men and women. Adequate intake of vitamin K can usually be achieved through a balanced diet that includes a variety of vitamin K-rich foods.
Why MenattoTM
Natural Vitamin K2
MenattoTM is produced through a natural fermentation process using B. subtilis natto, a non-GMO strain used in the production of the traditional Japanese food natto. Made from fermented soybeans, natto is naturally rich in vitamin K2 (MK-7), with 500 times higher concentration than the next-highest food source.
Natural matters to consumers. A 2018 survey of over 1,000 adults found that most respondents prefer natural to synthetic dietary supplements. Only 8% of respondents said they would purchase synthetic supplements if they were so labeled.

Clinically Researched Vitamin K2
MenattoTM is supported by a robust portfolio of clinical research. It is backed by ten well-controlled human clinical trials, all published in peer-reviewed scientific journals. This research demonstrates that MenattoTM:
・Supports healthy bone mineral density in post-menopausal women*
・Supports healthy bone mineral density in middle-aged men and women*
・Helps maintain bone health in post-menopausal women*
・Supports proper calcium metabolism in children*
・Supports healthy blood vessel elasticity*
・Achieves more stable and higher blood levels of vitamin K than vitamin K1
Original Fermented Vitamin K2
Sales of vitamin K2 finished products have increased exponentially over the past few years and the trend is expected to continue through 2025. This is due to increased awareness of its enhanced bioavailability compared to vitamin K1. As a result, many vitamin K2 ingredients have entered the marketplace.
MenattoTM is the original fermented vitamin K2 (MK-7) ingredient. J-Oil Mills was the first company in the world to develop a patented fermentation process for manufacturing vitamin K2 (MK-7) in 1997. Since then, J-Oil Mills has been consistently producing MenattoTM and supplying it to dietary supplement and functional food companies across the globe.

Authentic Japanese Vitamin K2
Japan is the birthplace of natto, where millions of people consume the sticky delicacy daily for breakfast over a bed of rice. Particularly well-loved in Eastern Japan, natto is considered Japanese soul food. It is only fitting, then, that natto-derived vitamin K2 be made by its culture of origin.
MenattoTM is the authentic Japanese vitamin K2. It is the only vitamin K2 (MK-7) that is made in Japan, and it may be labelled that way on finished products.
Fully traceable Vitamin K2
Traceability has surged in importance to consumers in recent years. In a 2020 survey, 73% of respondents said that traceability of products is important to them. Among those who said traceability is very important, 71% were willing to pay a premium for it.
As a vertically integrated company, J-Oil Mills can trace all phases of MenattoTM production, from procurement of raw materials to manufacturing to distribution, meeting our customers and end consumers’ need for traceability
How menatto® works?

Bone
Bones are not static; they are made of metabolically active tissue that is constantly reinventing itself. Through the process of remodeling, old bone tissue is broken down and new bone tissue is formed through the deposition of minerals into the skeleton.
Vitamin K2 helps calcium attach to bone by helping maintain the proper level of carboxylated osteocalcin, a protein that helps regulate calcium binding. As a result, it supports healthy bone density and helps build strong bones.* MenattoTM vitamin K2 has been shown in double-blind, randomized clinical trials to support bone health in people of all ages, from childhood, a crucial time during which most bone formation occurs, to post-menopause.

Heart
Elastic blood vessels allow the free flow of blood through the body and are essential for overall cardiovascular health.
Vitamin K2 helps regulate MGP (Matrix GLA protein) in the blood vessel wall.* This action helps maintain blood vessel elasticity, supporting healthy blood flow and cardiovascular health.* Original clinical research using MenattoTM vitamin K2 shows it supports arterial flexibility in healthy post-menopausal women.*

Joints
Cartilage is an important element of synovial joints. By covering the bones that meet in a joint with a slippery, flexible surface, cartilage allows them to glide against each other seamlessly, thus creating fluid motion. Various factors — including overexertion, natural ageing, and normal wear and tear — can affect the integrity of cartilage.
Vitamin K carboxylates proteins that support joint and cartilage health, such as matrix GLA protein and growth-arrest-specific-protein 6.* Preclinical research indicates this action supports collagen, the main component of cartilage, and helps chondrocytes (cartilage cells) differentiate and survive.*
Observational studies have noted that vitamin K status is associated with joint health.* Another reason for this link may be that vitamin K helps to regulate calcium deposits in soft tissue such as cartilage, which helps keep it flexible.*

Blood
Vitamin K plays a role in normal blood coagulation by helping to regulate both coagulation and anticoagulation as needed.* Prothrombin is a vitamin K-dependent protein (VKDP) that converts to thrombin (a clotting agent) when blood coagulates. Protein C, another VKDP, breaks down proteins into polypeptides and acts as an anticoagulant. Without vitamin K, neither protein can be activated.*

Beauty
Collagen is a component of connective tissue found in the skin. It is well-established that collagen production declines with age, which can cause the skin to become less firm and elastic.
Vitamin K2 has been shown to support collagen synthesis in human fibroblasts, the most common cells of connective tissue.* Through this action, may support healthy skin.* When collagen is broken down, the amino acids are used to form new proteins. Theoretically, this could increase the production of keratin, thereby supporting healthy hair and nails.*
K + D + Ca
How Vitamin K, Vitamin D and Calcium work together to build Bone Health
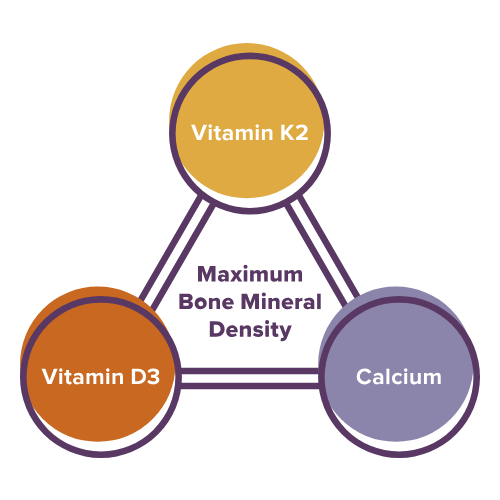
Just as a three-legged stool cannot balance without all three legs, bones cannot achieve optimal strength without all three of the following nutrients: vitamin K, vitamin D, and calcium.
Bone Density Trio
Vitamin K
Vitamin K activates at least 17 different proteins within the body. In terms of bone metabolism, the two most important VKDPs are:
・Osteocalcin, which helps calcium bind to the bone*
・Matrix GLA protein, which directs calcium toward the bones and away from the soft tissues*
Vitamin D
Vitamin D and vitamin K both play a role in delivering calcium to bone.* Vitamin D regulates calcium metabolism; it is necessary for the absorption and utilization of the mineral. In addition, vitamin D promotes the production of vitamin K-dependent proteins (VKDPs).
Calcium
Calcium is the nutrient most associated with bone health, probably because just under two-thirds of bone tissue is made of calcium salts. Since bone is living tissue, it is always being resorbed (broken down) and ossified (reformed) — a process known as remodelling. Therefore, a constant supply of calcium is needed to support proper bone mineral density (BMD).
Better Together
For osteocalcin to help regulate calcium binding, it must be in its carboxylated form. Taking calcium with vitamins K and D has been shown to support healthy levels of carboxylated osteocalcin and to support bone mineral density.*
In one study, researchers tested calcium + vitamin D supplements against calcium + vitamin D + vitamin K supplements. While both interventions supported overall bone mineral density, the supplement with vitamin K was effective in more parts of the body*
mechanism of action
17 different proteins in the body rely on vitamin K for their activation. These are called vitamin K-dependent proteins or VKDPs. Nearly all the effects of vitamin K on the body — whether on blood clotting, bone mineralization, blood vessel elasticity, or the maintenance of healthy cartilage — are due to its role in carboxylating, or activating, VKDPs.

Blood Coagulation and Anticoagulation
Prothrombin is a VKDP found in the blood that converts to thrombin (a clotting agent) during coagulation. Protein C is another VKDP that acts as an anticoagulant by breaking down proteins into polypeptides. Playing a role in both coagulation and anticoagulation, vitamin K contributes to normal blood coagulation.*
Cardiovascular Health
Vitamin K2 activates matrix GLA protein, which supports healthy blood vessel elasticity. * When arteries are flexible, blood can flow freely throughout the body, supporting overall cardiovascular health. *
Joint and Cartilage Health
Vitamin K carboxylates proteins involved in joint and cartilage health, such as matrix GLA protein and growth-arrest-specific protein 6.* Pre-clinical studies suggest this action supports collagen (which comprises about two-thirds of the dry weight of cartilage) and helps chondrocytes (cartilage cells) differentiate and survive, thus supporting joint health.*
In addition, pre-clinical studies indicate vitamin K helps to regulate calcium deposits into soft tissue, supporting joint health by keeping cartilage healthy and flexible. *
Bone Strength and Formation
In its carboxylated form, the protein osteocalcin helps calcium adhere to bone, thus maintaining bone strength.* Original clinical research on menatto® vitamin K2 shows it supports bone health in prepubertal children, adults 20-69, and post-menopausal women by supporting a healthy ratio of uncarboxylated, or inactive, osteocalcin (ucOC) to carboxylated, or active, osteocalcin (cOC).*
Vitamin K also supports endochondral bone formation (bone formation from cartilage in fetuses and children) by supporting the production of the VKDPs osteocalcin and matrix GLA protein. *
Beauty
Vitamin K2 binds to the steroid and xenobiotic receptor (SXR). This action helps regulate gene activity related to the extracellular matrix (the noncellular components of tissue that act as scaffolding for cells).* One of the genes that vitamin K2 upregulates is involved in collagen production.* In fact, vitamin K2 has been shown to support collagen synthesis in human fibroblast and osteoblast cells.*

